Liver inflammatory injury induced by IR and therefore indicated another mechanism of clinical good performance of anti-CD25 mAb in transplantations besides organ tolerance induction. Liver ischemia-reperfusion injury occurs in the clinical settings of hepatic resection surgery, hemorrhagic trauma, and liver transplantation. In the last 20 years, the rates of acute and chronic rejection have fallen dramatically, for example, the incidence of acute rejection during the first six months post-transplant has declined from over 40% in 1995 to around 15% in 2000. Part of this improvement results from increased use of selective induction agents, particularly the interleukin-2 receptor antagonists. Addition of anti-CD25 mAb to a variety of calcineurin inhibitor-based immunosuppressive regimens reduced acute rejection by 30�C50% as reported in two meta-analyses of the randomized controlled trials. These meta-analyses also demonstrated trends toward improved graft survival with anti-CD25 mAb compared with no induction. Although the protective effect for induction therapy of anti-CD25 mAb has been widely documented in liver transplantation field, the exact effect of anti-CD25 mAb on liver IR injury, however, remains poorly elucidated. The present study for the first time demonstrated that antiCD25 mAb administration shortly antecedent to liver IR induction provides protection in the initiation phase of injury. After 70% liver ischemia, anti-CD25 mAb pretreated mice displayed Ascomycin significantly preserved liver function as characterized by less histological damage and reduced serum enzymes level. We further demonstrated that the protective effect was associated with ameliorated intrahepatic inflammatory milieu and reduced CD4 + T lymphocytes as manifested by the decrease of Metyrapone proinflammatory cytokine production and the lower CD4/CD8 proportion. By employing an in vitro lymphocytes proliferation assay model, we confirmed that the protective effect of near-term antecedent anti-CD25 mAb treatment on IR-induced liver injury depend on the inhibition on the proliferation of CD4 + T lymphocytes. Taken together, our data demonstrated that near-term antecedent anti-CD25 mAb treatment provides protection for livers against subsequent IRinduced injury by inhibiting the proliferation of CD4 + T lymphocytes and mitigates intrahepatic inflammatory milieu through decreasing the proinflammatory cytokine production. Our data presented in the current report are in agreement with previous studies in the lung, kidney and brain after IR induction.  These results suggested that this brisk response, which preceded the influx of innate immune cells to the injured tissue, is mainly associated with resident T lymphocytes. These organ-resident T lymphocytes can maintain the expression of specific cytokine receptor on their cell surface and proliferate in vivo in the absence of Ag stimulation. It has been previously demonstrated that use of MHC-IIblocking antibodies has no effect on serum alanine transaminase following hepatic IR, which suggested that T cells play a role not involving the ab TCR and that lymphocyte actions occur through a non-antigenic mechanism. Treg is known as a critical role in maintaining immune homeostasis. In the model of IR injury, Treg functions to restrain excessive Teff cell responses. In line with the studies of depletion kinetics of PC61, the near-term administration of PC61 did not modify the number of Tregs significantly, and the depletion of CD4 + FoxP3 + Tregs in PC61-treated mice was already apparent 4 days after injection.
These results suggested that this brisk response, which preceded the influx of innate immune cells to the injured tissue, is mainly associated with resident T lymphocytes. These organ-resident T lymphocytes can maintain the expression of specific cytokine receptor on their cell surface and proliferate in vivo in the absence of Ag stimulation. It has been previously demonstrated that use of MHC-IIblocking antibodies has no effect on serum alanine transaminase following hepatic IR, which suggested that T cells play a role not involving the ab TCR and that lymphocyte actions occur through a non-antigenic mechanism. Treg is known as a critical role in maintaining immune homeostasis. In the model of IR injury, Treg functions to restrain excessive Teff cell responses. In line with the studies of depletion kinetics of PC61, the near-term administration of PC61 did not modify the number of Tregs significantly, and the depletion of CD4 + FoxP3 + Tregs in PC61-treated mice was already apparent 4 days after injection.
Month: May 2019
The normal variability of the human plasma proteome from healthy subjects individuals
Because of dynamic range, reproducibility and throughput limitations, 2D gel electrophoresis was surpassed by bottom-up and top-down mass spectrometry approaches for decoding protein modifications. In bottom-up approaches, proteins are digested with trypsin, and selected reaction monitoringor multiple reaction monitoringmass spectrometry is used to detect peptidesthat contain the protein modifications. Osteopontin splice variants were identified and quantified using MRM-MS ; novel proteoforms of prostate specific antigen were also identified in clinical samples via MRM-MS. In a larger population study, the concentration of three selected single amino acid polymorphism peptides, representing the Complement Component C7, Complement Factor H, and Complement Component C5 proteins, were measured by SRM-MS from 290 individuals. In another population study, serum peptide variations were studied in 500 healthy individuals using a regular MS analysis, but the peptides detected were exopeptidase products derived from relatively abundant serum proteins. Top-down MS approaches provide more accurate and complete results for protein variants identification because 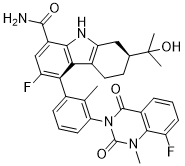 there is no Cefetamet pivoxil HCl prerequisite for a priori knowledge of the protein modification in order to select the appropriate modification-specific peptide. But analyzing and quantifying intact proteins and their modifications with mass spectrometry can be challenging. Our group has devised a simple method termed mass spectrometric immunoassaythat combines a one-step affinity protein isolation with MS analysis that is ideally suited for high-throughput analysis of human plasma proteins and their variants. Antibodies are surface-immobilized in small, porous microcolumns that are fitted at the entrance of a pipettor tip. Samples are passed through the pipette tip repetitively until enough protein is bound to the antibody. Following washing with buffer and/or other mild solutions to remove non-specifically bound sample components, the proteins are eluted with a small volume of matrix solution and deposited directly onto a MALDI target for ensuing MS analysis. We’ve applied this approach to investigate the diversity of 25 human plasma proteins from a cohort of 96 healthy individuals, resulting in the detection of 76 structural variants, each occurring with different frequencies. Subsequently, we’ve screened 1,000 individuals from four geographical regions in the United States, and determined the variants and their frequencies for five proteins – beta-2-microglobulin, cystatin C, retinol binding protein, transferrin, and transthyretin. The qualitative data from those studies provided a first glimpse into the extent of protein structural diversity in the general population. Recently we have Albaspidin-AA developed and validated fully quantitative mass spectrometric immunoassays for 4 of those clinically relevant proteins – beta-2-microglobulin, cystatin C, retinol binding proteinand transthyretin. Beta-2-microglobulin is used in the diagnosis of active rheumatoid arthritis and kidney disease, and a structural variant of b2m has been associated with autoimmune disease and small-cell lung cancer. Cystatin C is a serine proteinase inhibitor with implications in renal failure. Retinol binding protein has also been implicated in renal disease, with the increased presence of its truncated variants suggested as indication of renal failure.
there is no Cefetamet pivoxil HCl prerequisite for a priori knowledge of the protein modification in order to select the appropriate modification-specific peptide. But analyzing and quantifying intact proteins and their modifications with mass spectrometry can be challenging. Our group has devised a simple method termed mass spectrometric immunoassaythat combines a one-step affinity protein isolation with MS analysis that is ideally suited for high-throughput analysis of human plasma proteins and their variants. Antibodies are surface-immobilized in small, porous microcolumns that are fitted at the entrance of a pipettor tip. Samples are passed through the pipette tip repetitively until enough protein is bound to the antibody. Following washing with buffer and/or other mild solutions to remove non-specifically bound sample components, the proteins are eluted with a small volume of matrix solution and deposited directly onto a MALDI target for ensuing MS analysis. We’ve applied this approach to investigate the diversity of 25 human plasma proteins from a cohort of 96 healthy individuals, resulting in the detection of 76 structural variants, each occurring with different frequencies. Subsequently, we’ve screened 1,000 individuals from four geographical regions in the United States, and determined the variants and their frequencies for five proteins – beta-2-microglobulin, cystatin C, retinol binding protein, transferrin, and transthyretin. The qualitative data from those studies provided a first glimpse into the extent of protein structural diversity in the general population. Recently we have Albaspidin-AA developed and validated fully quantitative mass spectrometric immunoassays for 4 of those clinically relevant proteins – beta-2-microglobulin, cystatin C, retinol binding proteinand transthyretin. Beta-2-microglobulin is used in the diagnosis of active rheumatoid arthritis and kidney disease, and a structural variant of b2m has been associated with autoimmune disease and small-cell lung cancer. Cystatin C is a serine proteinase inhibitor with implications in renal failure. Retinol binding protein has also been implicated in renal disease, with the increased presence of its truncated variants suggested as indication of renal failure.