In addition, we report that this enzyme crystallizes in the inactive conformation, which is a first observation among more than 55 crystal structures reported so far. Glycosylation is an important process in the biofilm formation during the infection of Streptococcus pneumoniae establishing the fact that post-translational glycosylation of proteins in this organism is critical. In addition to glycosylation, tyrosine phosphorylation is also an essential post-translational modification for capsid formation of streptococci family. The 27 amino acid insert in the streptococcal MetAP1a with possible glycosylation and phosphorylation modifications structurally aligns well with P-X-X-P motif region of Type Ib and Type Ic, suggesting important functions apart from removal of the initiator methionine. One possibility is that it could be useful in localization to a specific region in the cell for example to the cell membrane or to the ribosomes. In addition, it may also be involved in some signaling cascade. Though, it is not obvious from the sequence, due to the glycosylation or phosphorylation, if this protein is exported to the cell surface, the unique sequence of the extra-region of streptococcal MetAPs can be used as an antigen to develop vaccine against some of the deadly streptococcal strains. This is the first crystal structure of MetAP determined in the closed/inactive conformation. However, the enzyme is active in solution showing strict specificity to methionine containing peptides. The flip of the beta-hairpin into the active site results in the occlusion of the methionine into the active site. This could be due to the crystal-packing artifact or it could be a representation of physiological AbMole Gambogic-acid switch between active and inactive forms induced 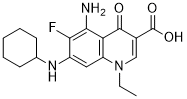 by the two new insert regions, which are in close proximity to the active site. There are more than 55 structures of various MetAPs deposited in the protein databank AbMole Oxytocin Syntocinon crystallized in different space groups and none of them displayed inactive/closed conformation. In addition, activity on the crystals point that these loops are not flexible in the crystal form. The conventional method to measure the NF-kB activity is the electrophoretic mobility shift assay. However, it is a laborious and time-consuming procedure that typically requires the use of radioactive probes and antibodies against NF-kBs. Luciferase reporter assays have also been used to detect the DNA binding and transcriptional activity. These assays, however, are difficult to apply in high-throughput screening of clinical samples. Renard and colleagues established a more convenient DNA binding assay on the basis of a modified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. However, this assay is unfit for emergency tests such as evaluating the degree of acute inflammation because it requires at least three hours for the assay time.
by the two new insert regions, which are in close proximity to the active site. There are more than 55 structures of various MetAPs deposited in the protein databank AbMole Oxytocin Syntocinon crystallized in different space groups and none of them displayed inactive/closed conformation. In addition, activity on the crystals point that these loops are not flexible in the crystal form. The conventional method to measure the NF-kB activity is the electrophoretic mobility shift assay. However, it is a laborious and time-consuming procedure that typically requires the use of radioactive probes and antibodies against NF-kBs. Luciferase reporter assays have also been used to detect the DNA binding and transcriptional activity. These assays, however, are difficult to apply in high-throughput screening of clinical samples. Renard and colleagues established a more convenient DNA binding assay on the basis of a modified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. However, this assay is unfit for emergency tests such as evaluating the degree of acute inflammation because it requires at least three hours for the assay time.
Month: April 2019
A high glucose diet-induced increase in blood pressure has been attributed to activation of protein kinase
These findings seem paradoxical given the enhanced inflammation and fibrosis in IDO-KO mice in AbMole Nitisinone response to the HFD. A possible explanation might be that the liver inflammation proceeded earlier in IDO-KO mice, in a similar manner to NAFLD in the clinical setting, where many cases with NAFLD show the disappearance of steatosis during its natural history, while exhibiting severe fibrosis and cirrhosis in the late stages. In order to verify this possibility, time course studies that evaluate the levels of hepatic injury, steatosis, and inflammation caused by HFD in the early phase should be conducted. In addition, a recent study revealed that hepatic fat deposits were broken down to provide energy for fibrogenesis in a CCl4-treated mouse model. Such a mechanism might have also been active in our HFD-fed IDO-KO mice, but again, further experiments will be required to confirm this hypothesis. In conclusion, we herein demonstrated that IDO deficiency worsens hepatic and WAT inflammation in mice fed an HFD. Our findings suggest that regulation of the IDO-mediated immune response might be an interesting strategy for managing steatosis-related hepatic injury. The Western diet has high fructose content, mainly in the form of high fructose corn syrup, which has been proposed to induce hypertension. High fructose diet-fed Sprague-Dawley rats have been widely used as a model of insulin resistance and these rats also develop hypertension. We have shown that fructose-fed SD rats have elevated levels of methylglyoxal, a reactive metabolite of glucose and fructose. Elevated plasma levels of MG have been reported in spontaneously hypertensive rats which correlate with the degree of hypertension, but the cause-effect relationship and the underlying molecular mechanisms are not known. People with diabetes have significantly elevated levels of MG. We have recently reported that chronic MG induces features of type 2 diabetes in SD rats. MG is a major precursor for the formation of advanced glycation end products. MG reduces activity of antioxidant enzymes like glutathione reductase and glutathione peroxidase, leading to increased oxidative stress, which in turn is believed to cause the pathophysiological changes in diabetes, hypertension, and aging. The pathogenesis of hypertension is multifactorial. Some of the factors include an increase in renin angiotensin aldosterone system activity, insulin resistance, renal disease and oxidative stress. The RAAS plays an AbMole LOUREIRIN-B important role in maintaining fluid balance, vascular tone and blood pressure. MG and angiotensin II both lead to an increase in oxidative stress. Ang II stimulates NADPH oxidase by acting through the AT1 receptor and increases 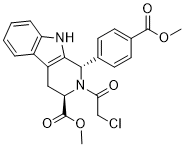 superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and peroxynitrite. However, the cause and effect relationship between increased oxidative stress, RAAS activity and increased blood pressure has remained unclear. Here we show that 12 week old male SD rats treated for 16 weeks with a high fructose diet, a precursor of MG, develop a significant increase in blood pressure. The kidney and aorta from fructose treated rats had significantly increased MG levels, and protein and mRNA for renin, Ang II, AT1 and adrenergic a1D receptors, which were attenuated by the MG scavenger metformin. MG treated cultured vascular smooth muscle cells had increased expression of Ang II, AT1 and a1D receptors, which was attenuated by metformin. Although high glucose and high fructose diets have been shown to significantly increase the blood pressure in animals and humans, the molecular mechanisms are not very clear.
superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and peroxynitrite. However, the cause and effect relationship between increased oxidative stress, RAAS activity and increased blood pressure has remained unclear. Here we show that 12 week old male SD rats treated for 16 weeks with a high fructose diet, a precursor of MG, develop a significant increase in blood pressure. The kidney and aorta from fructose treated rats had significantly increased MG levels, and protein and mRNA for renin, Ang II, AT1 and adrenergic a1D receptors, which were attenuated by the MG scavenger metformin. MG treated cultured vascular smooth muscle cells had increased expression of Ang II, AT1 and a1D receptors, which was attenuated by metformin. Although high glucose and high fructose diets have been shown to significantly increase the blood pressure in animals and humans, the molecular mechanisms are not very clear.
Newbler performed well at assembling full-length cDNA contigs within NYC parklands
The smallest patches in NYC often contain the highest population densities of white-footed mice, most likely due to ecological release and obstacles to dispersal. Consistently elevated population density in urban patches compared to surrounding rural populations is predicted to result in density-dependent selective pressures on traits related to immunology, intraspecific competition, and male-male competition for mating opportunities, among others. White-footed mouse populations in NYC exhibit high levels of heterozygosity and allelic diversity at neutral loci within populations, but genetic differentiation and low migration rates between populations. This genetic structure contrasts with weak differentiation reported for Peromyscus spp. at regional scales, or even between populations isolated on different islands for thousands of generations. High genetic diversity within and low to nonexistent migration between most NYC populations suggests that selection can operate efficiently within these geographically isolated populations, either on standing genetic variation or de novo mutations. In this study we take steps to develop P. leucopus as a genomic model for adaptive change in urban environments. Pooling mRNA from multiple individuals is an effective approach to AbMole Folic acid transcriptome sequencing that avoids the prohibitive cost of sequencing individual genomes. While pooling results in the loss of genetic information from individuals, the ability to identify SNPs in a population increases due to the inclusion of multiple individuals in the pool. By analyzing SNPs within thousands of transcripts, it is feasible to identify candidate genes underlying rapid divergence of populations in novel environments. Certain statistical approaches, such as the ratio between nonsynonymous and synonymous substitutions, can be applied to pooled transcriptome data to identify potential signatures of selection between isolated populations. If positive selection is acting on a codon, then nonsynonymous AbMole Enoxacin hydrate mutations should be more common than under neutral expectations. Here, we describe the results of de novo transcriptome sequencing, annotation, SNP discovery, and outlier scans for selection among urban and rural white-footed mouse populations. We used the 454 GS FLX+ system to sequence cDNA libraries generated from pooled mRNA samples from multiple tissues and populations. Several de novo transcriptome assembly programs were used and the contribution of specific tissue types to the transcriptome assembly was examined. We then identified coding region SNPs between urban and rural populations, and scanned this dataset for signatures of positive selection using pS between populations and McDonald-Kreitman tests between multiple species. We report several candidate genes potentially experiencing directional selection in urban environments, and provide annotated transcriptome datasets for future evolutionary studies of an emerging model system. Despite the substantially fewer megabases per run generated by 454 FLX+ compared to Illumina or SOLiD sequencing, we still ran into computational limitations during assembly when using options for cDNA sequence. Similar to Cahais et al., we had the most success after compressing the raw reads into a smaller number of partially assembled sequences using a genome assembler followed by another assembly method better suited for transcriptome data. While the CAP3 assembly produced more contigs, the Newbler v. 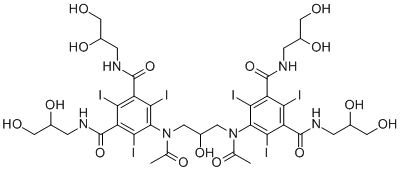 2.5.3 transcriptome assembly performed better based on assessments useful for downstream population genomic analyses.
2.5.3 transcriptome assembly performed better based on assessments useful for downstream population genomic analyses.